With the development of science and technology, medical endoscopes have been widely used in the medical field. It is one of the important tools for humans to peep and treat human internal organs.
The structure of the endoscope has undergone four major improvements in the development of more than 200 years, from the original rigid tube endoscope (1806-1932), semi-flexed endoscope (1932-1957) to fiber endoscope Mirror (after 1957), and now the electronic endoscope (after 1983). The image quality has also undergone an inferior leap.
In 1806, Bozzini of Frankfurt, Germany made a candle as a light source for observing the inside of the bladder and rectum; with the development of science and technology, it changed to a light bulb as the light source. Today, LED lighting is used, and the endoscope obtains color photos or Color television image. The images are no longer ordinary images of tissues and organs, but are like microscopic images observed under a microscope. The tiny lesions are clearly distinguishable, and the image quality has reached a high level.
The clinical application of medical endoscopes is becoming more and more popular, and it is developing towards miniaturization, multi-function and high image quality. The following introduces the classification, composition, structure, working principle, clinical application and development trend of medical endoscopes.
01
definition
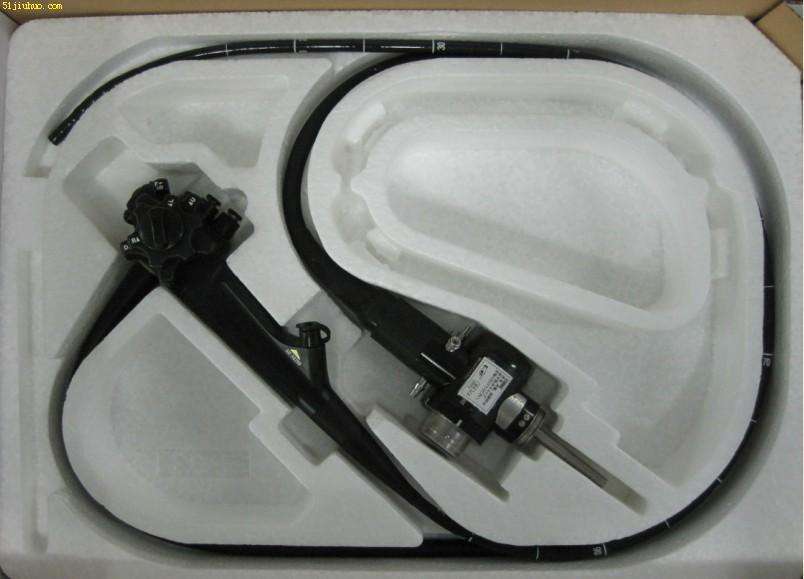
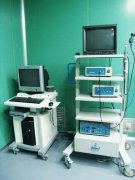
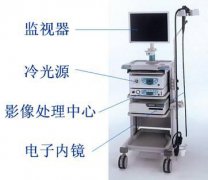
A medical endoscope is a commonly used medical device, which consists of a flexible part, a light source and a set of lenses. It enters the human body through the natural pores of the human body or through a small incision made by surgery. When in use, the endoscope is introduced into the organ for pre-examination, and the changes in the relevant parts can be directly observed.
02
Classification of medical endoscopes
According to its imaging structure classification: can be roughly divided into three categories: hard tube endoscope; optical fiber endoscope (can be divided into soft and hard); electronic endoscope (can be divided into soft and hard) );
03
Related parameters and faults
(1) Common failures of light source system
(A) Dim light. Excluding the cause of the grating occlusion, it is basically certain that the bulb is approaching its service life, and it can be replaced with a new bulb. The service life of the xenon bulb is generally designed to be 500 hours. If the light source system has a life timer device, this problem can be easily solved.
(B) The bulb does not light up when turned on. If the reason for burning the bulb is ruled out, then the problem often lies in the high-voltage ignition circuit of the main engine, because the machine will generate tens of thousands of volts pulse high voltage when the machine is turned on, and the components will age very quickly. Note that you cannot use a multimeter to check the pulse high voltage at this time.
(2) Common faults of artificial pneumoperitoneum system
(A) The pressure display is incorrect. This is mostly due to the damage of the gas pressure sensor. If the machine is designed with a group of multiple differential pressure sensors working at the same time, generally when one is aging or contaminated and cannot work, we have to replace all of this group of sensors, otherwise only one of them will be replaced, the others The life of the sensors in the same group is also approaching critical.
(B) Inaccurate flow. If the gas flow sensor is damaged, replace it. Sometimes the flow is calculated by the pressure difference, at this time we have to replace the new pressure sensor.
(C) Equipment leaks. Many cases are caused by the aging of the instrument sealing ring. However, there are also reasons for the leakage of the mechanical pressure reducing valve of the equipment and the damage of the solenoid valve. This is easier to judge and repair.
(3) Common failures of liquid pressurization system
(A) The peristaltic pump is damaged.
(B) The liquid pressure sensor is damaged. The principle is basically the same as the gas pressure sensor.
(C) The internal circuit of the equipment is damaged.
(4) Common faults of electrocoagulation and cutting system
(A) Equipment accessories are damaged. Such as foot switch, negative board lead, connecting lead and other commonly used vulnerable accessories.
(B) Electric cutting, electrocoagulation, bipolar failure. Inside the device, these parts are composed of different circuit modules. We can repair or replace the corresponding module circuit according to the fault phenomenon.
(5) Common failures of power and ablation systems
(A) The power system is mainly due to the wear of the planing cutter head and the high-energy motor in the planing handle. The replacement of the motor is selective, and not every motor has replacement parts. Therefore, special attention must be paid to protection during disinfection and use.
(B) The ablation system is mainly the loss of the blade in the surgical application. However, equipment failures are mostly circuit failures, and usually start from the output part.
(6) Common faults of flushing suction system
(A) Insufficient pressure or suction. The two-way pump in the equipment is aging, or the negative pressure bottle is leaking.
(B) The equipment cannot be turned on. Generally, liquid enters the equipment. It is enough to clean up the misabsorbed liquid without burning the relevant parts.
04
summary
In order to minimize the occurrence of equipment failures, a dedicated laparoscopic operating room should be set up to reduce the movement and damage of the instrument, and a specialist nurse of endoscopy should be assigned to use and maintain it. The specialist nurse of endoscopy should be fully familiar with the performance and structural characteristics of the instrument and its accuracy The method of use, strictly implement the operating procedures, and pay attention to the three links of preoperative inspection, intraoperative troubleshooting, and timely postoperative maintenance. If there is a problem with the equipment, first take emergency repairs, because this can solve the small and medium faults that account for about 85% of the faults. The most difficult problem to solve during actual maintenance is the ordering of replacement parts. Manufacturers rarely sell accessories. If the equipment is damaged, it is better to deal with it, just go to the manufacturer directly.
At present, many hospitals also use domestic equipment. However, because the design level and production technology have not reached the international advanced level, it is relatively easy to be damaged and the matching of the equipment is not enough. Usually, the same equipment of the same brand cannot be matched after replacement.
![]() Phone Number:0755-26943630
Phone Number:0755-26943630![]() Phone Number:0755-26943630
Phone Number:0755-26943630


![]()
