![]() Phone Number:0755-26943630
Phone Number:0755-26943630
![]() Phone Number:0755-26943630
Phone Number:0755-26943630

Time:2020-07-25 23:38 Click:/Second

With the wide application of medical endoscopes in medical diagnosis and treatment, the characteristics of precision miniaturization, integration and customization, and one-time use of endoscopes ...
Without causing tissue trauma, a small endoscopic probe is a necessary equipment for imaging small cavities or fragile organs. However, current manufacturing methods limit the imaging performance of highly miniaturized probes, thereby limiting the wide ap...
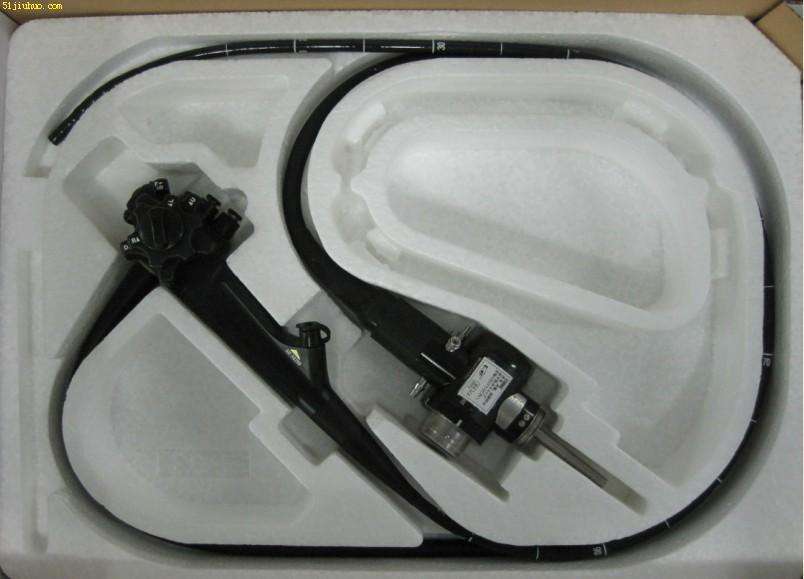

Put the endoscope with a fully automatic perfusion device and various buttons in the disinfectant, and the endoscope performs fully automatic throughflow. The operating parts of the full-immersion endoscope must all be immersed in the disinfectant....
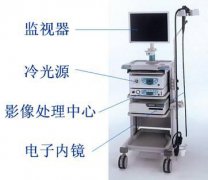
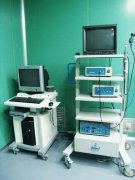
The endoscope equipment system will be called differently when it is used in various clinical departments, such as: ventriculoscopy, thoracoscopy, hysteroscopy, uretero-nephroscope, resection of the prostate, intervertebral discs, ...
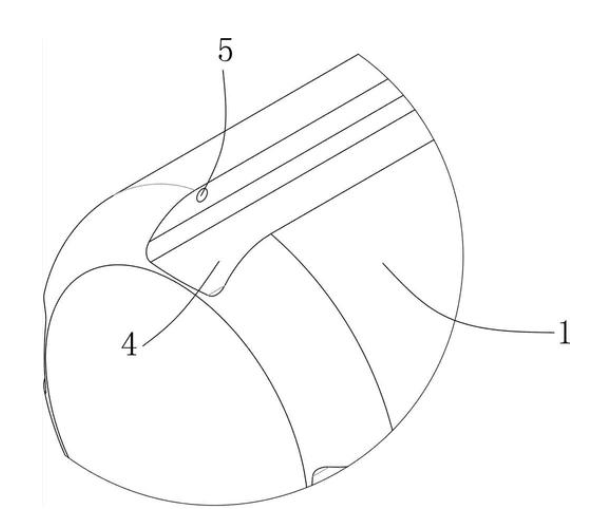
With the wide application of medical endoscopes in medical diagnosis and treatment, precision miniaturization, integration and customization, and the characteristics of disposable endoscopes will become the future development trend of the industry. ...
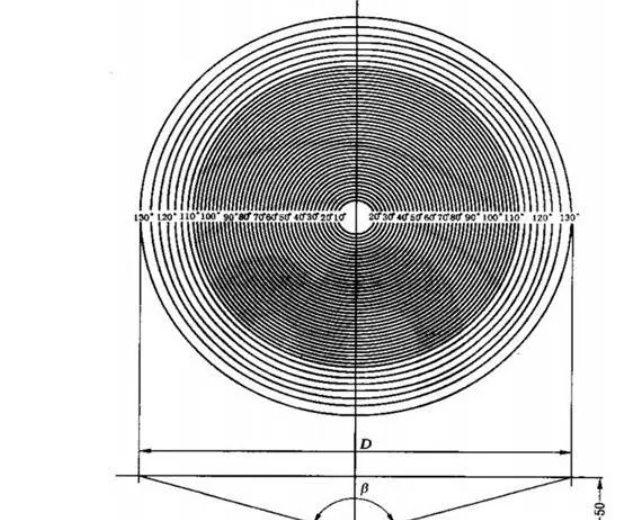
The field of view and the viewing angle of the medical rigid endoscope are two very important optical performance parameters, which will directly affect the position and range of the observation object when the medical rigid endoscope is used. The measure...
![]()
